Contents
Temaşevanê fîlimê X-ray: ew ji bo çi ye, kengî tê bikar anîn?
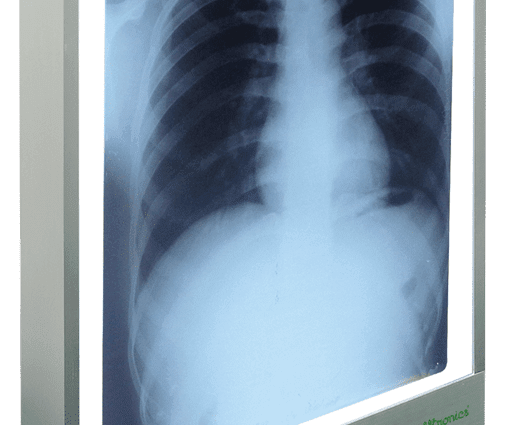
Negatoscopes are one of the essential medical imaging instruments that can be found in operating theaters, emergency rooms or medical offices. The reading of x-ray images by radiologists, specialist or general practitioners is an essential step in establishing a diagnosis and taking charge of the pathology highlighted.
What is a negatoscope?
The negatoscopes are backlit luminous tables which make it possible to read X-rays through transparency. Diffused lighting is similar to natural light. The reading accuracy of the X-ray image and the accuracy of the resulting diagnosis depend directly on the quality of this lighting.
Pêkhatîya
Conventional negatoscopes are kinds of boxes, one of the long sides of which is a backlit translucent glass. This pane allows light to be evenly distributed over its entire surface.
The negatoscopes are available in different sizes with 1 to 4 reading ranges, which can be switched on together or separately. Their size is suitable for most x-rays of adults or children. Power is supplied from the mains by an on / off button. On some models, the light intensity can be modulated by a dimmer allowing the power of the transmitted light to be modified. The color temperature of fluorescent tubes is between 6100 and 7220 Kelvins. The negatoscopes are available in a vertical model to hang on the wall or in a horizontal model to put on a desk stand.
What is a X-ray viewer for?
Taking an x-ray is a very common step taken to establish or confirm a diagnosis. These are quick and easy exams to perform. The patient is subjected to a beam of X-rays. The electrons, which pass through the body, are more or less attenuated according to the density of the tissues or organs crossed.
Reading x-rays
- Very dense tissues, such as bones, strongly attenuate the X-ray beams which pass through them: they appear white in color on the photograph;
- Intermediate density tissues, such as muscles, moderately attenuate X-rays: they appear greyish on the X-ray;
- Low density tissue, such as water or air, hardly attenuates the x-ray beam: they appear dark in color on the image.
The image of internal tissues collected on the x-ray film can therefore be compared mentally to a “normal” image. Any abnormally present stain will potentially be synonymous with pathology.
Interpretation of radiographs
In orthopedic surgery, X-rays make it possible to highlight the various possible lesions of the musculoskeletal system:
- şikandina hestî;
- damage to the cartilage of the joints;
- rijandina tendon;
- hwd.
X-rays can also diagnose:
- têkçûna dil;
- a pneumonia ;
- tumor;
- emfîzema pişikê;
- astengiya rûvî;
- iltîhaba cûda;
- hwd.
How is a x-ray viewer used?
Qonaxên operasyonê
The practitioner places the X-ray image he wants to read on a plate of the X-ray viewer and turns on the corresponding plate. In the case of vertical negatoscopes, the images are “clipped” into a groove located at the top of the glass. The reading is done by transparency thanks to lighting by fluorescent tubes which diffuse a light similar to natural light.
Kengê bikar bînin?
X-rays are used to read X-ray images in many hospital departments and in doctor’s offices.
Maintenance of the x-ray viewer
To keep the X-ray viewer working properly and to ensure the best possible reading of the X-rays, several parameters must be checked regularly:
- the cleanliness of the glass;
- the brightness, which must remain homogeneous over the entire surface of the pane;
- the temperature of the tubes, which must be regularly checked in order to detect any lighting anomalies.
How to choose a light box?
The different models of negatoscope
- The classic X-ray X-ray viewer: this is the standard model found in hospitals or doctors’ offices. It is activated manually by one or more switches which enable the reading range (s) to be switched on. These ranges can be lit separately or simultaneously. Some models are equipped with a dimmer;
- The extra-flat model offers a very homogeneous lighting mode with no stroboscopic effect (flashing of the light). It has 1 to 4 ranges and has a dimmer;
- The automatic X-ray viewer: the switch-on is done automatically when a picture is placed. The lights come on one by one;
- The dental x-ray viewer allows dentists and orthodontists a very fine reading of dental x-rays: panoramic x-rays, retro-alveolar x-rays, long-cone assessments;
- The “new generation” medical X-ray viewer guarantees strong and perfectly homogeneous luminosity. Its materials are extremely robust and its longevity almost infinite. Its electronic components meet very strict standards. All of this makes it a very stable light box. On some models, the light intensity can be adjusted by a dimmer. Models with integrated reflectors have an ergonomic and rational control box. The installation can be horizontal, vertical, and on a metal stand.
The criteria for choosing the right viewer
- The number of tracks: from 1 to 4 tracks most often, but there are models going up to 12 tracks and even more;
- the quality of light;
- the start command;
- compliance with safety standards;
- Nîşankirina CE.
Other uses of the X-ray viewer
We use negatoscopes in fields other than medical:
- in photography to read negatives or slides;
- in printing for mounting offset films or in screen printing;
- in graphic art to trace an image or make montages.